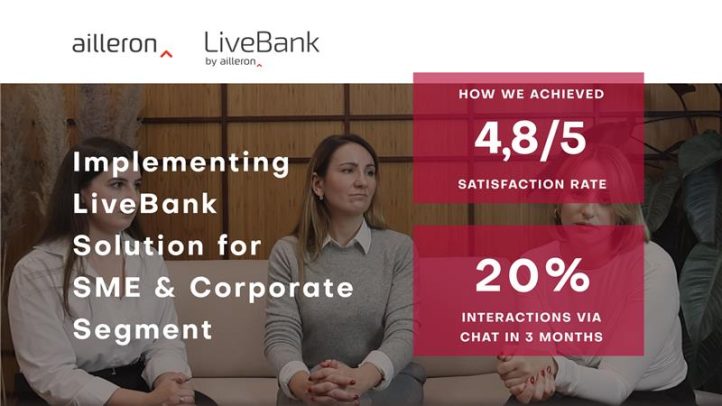
What challenges do banks face in this area? How can digital solutions be effectively implemented? This article presents key takeaways from the deployment of a modern SME service platform at ING, offering insights that can help other financial institutions navigate a similar transformation.
Table of Contents
Step 1: Identifying the Challenge
In the traditional banking model, SME clients often need to visit branches, submit paper documents, and go through lengthy formal procedures. In today’s fast-paced business world—where many SMEs operate primarily online—this approach has become an obstacle to efficient collaboration between banks and their clients.
During an analysis of banking processes at ING, three key pain points were identified:
- Limited access to advisors – clients wanted to communicate more efficiently with their bank without visiting a branch.
- Cumbersome document exchange – manual paperwork processing caused delays and inefficiencies.
- Lengthy contract finalization – requiring physical signatures slowed down transaction completion.
These insights laid the foundation for developing a more efficient service model tailored to the needs of dynamic SME clients.
Step 2: Addressing the Diversity of the SME Segment
One of the biggest challenges in SME banking is the wide variety of businesses, from sole proprietors to companies with dozens of employees. Different industries have unique needs, and bank advisors must tailor their approach accordingly.
At ING, an in-depth analysis of advisors’ daily work was conducted, gathering feedback on obstacles they encountered and potential improvements. The result was a new service model incorporating:
- Remote consultations via video conferencing and chat – eliminating the need for in-person visits.
- Secure real-time document exchange – reducing the reliance on printed paperwork.
- Electronic signatures – enabling swift contract finalization.
- CRM system integration – enhancing relationship management and personalized service.
This approach empowered advisors to provide more efficient service, while SME clients gained increased flexibility and convenience in their banking interactions.
Step 3: From Pilot Model to Full-Scale Implementation
To introduce modern banking solutions, ING adopted an evolutionary rather than revolutionary approach—gradual implementation ensured better control over the transformation process.
The first step was defining the target service model—how the process should function in two years and which initial changes would bring the most immediate benefits.
The Pareto principle was applied, focusing on key elements that would yield the greatest impact in the first phase while requiring minimal time and financial investment.
Key actions in this phase included:
- Testing with a selected group of advisors – verifying the effectiveness of new tools in daily operations.
- Pilot implementation (Proof of Concept, POC) – assessing how the technology performed in real-world conditions before full deployment.
- Gradual scaling of solutions – instead of rolling out changes across the organization all at once, a step-by-step approach was used, allowing for ongoing analysis and adjustments.
How did this transformation work in practice? Watch experts from ING’s SME segment share their insights on implementing modern banking solutions and the key lessons learned from the process.
Step 4: Training and Preparing the Team
Technology alone does not guarantee success—equally important is preparing the team to use it effectively.
As part of the LiveBank platform implementation at ING, the Ailleron team conducted comprehensive training sessions for advisors, focusing on:
- Understanding customer expectations – recognizing how SME business operations are evolving and how banking services should adapt.
- Practical use of new tools – advisors practiced real-life customer service scenarios in simulated environments.
- Optimizing client communication – leveraging video conferencing, online document exchange, and electronic signatures for seamless service.
The result was not just a technology rollout but also a shift in the customer service culture—advisors became more adaptable, and banking processes became faster and more transparent.
Key Takeaways for Banks Implementing Digital Solutions
The experience gained from ING’s implementation of a modern SME service model demonstrates that digitization in banking is not just about new tools – it’s about rethinking the customer service approach.
Key takeaways from this process include:
- Understanding real customer challenges – analyzing SMEs’ daily difficulties is essential for successful implementation.
- Adopting a gradual transformation approach – an evolutionary strategy increases the likelihood of success and enables better change management.
- Proof of Concept (POC) as a crucial step – testing before full deployment helps validate assumptions and minimize risks.
- Investing in training and cultural change – technology alone won’t deliver results without a well-prepared team.
For banks planning a similar transformation, digitization should be viewed as an ongoing process—introducing new technologies is just the beginning of improving SME customer service. For further details on ING’s case study presented at the Annual AIF (Ailleron Innovation Forum) Conference, click here.