Table of Contents
AI bots vs. customer service agents – customers’ preferences
Customers increasingly prefer remote communication channels. Research data shows that 47% of customers chose face-to-face contact before the pandemic. Today, only every fourth customer prefers face-to-face communication.
More calls are coming into contact centres, according to customer service leaders. Along with that increase, it is necessary to ensure the quality of communication with the customer and contain the amount of time each support instance takes. Along with the benefits of the banking products themselves, customers are becoming more sensitive to the level of service offered. On the other hand, for businesses, it all comes down to this question: “How can I handle more calls without increasing the number of employees?” The remedy for this turns out to be a technology that has already been on the market for some time: bots. Bots and AI in customer service were created precisely to respond to such needs. This is thanks to their ability to understand the client’s question and provide an answer based on pre-programmed conversation patterns and knowledge base.
Currently, the following types of bots are available:
- Voicebots – these bots use speech-to-text technology; they are most often used as part of optimization in the IVR channel or as a stand-alone service
- Chatbots – used as a form of customer service automation, often within a text messenger in the form of asynchronous communication
- Mailbots – used to easily automate email queries, which are still one of the most critical communication channels for banking institutions.
Each AI bot is developed to serve customers through three distinct channels of remote communication with the client: telephone, e-mail, and text. These tools are growing more advanced each year, but they are still far from being the most used communication channel with customers.
Why customers don’t entirely trust AI customer service bots in banks
From the customer’s side, there is still a lack of trust toward bot technology and AI customer service in banks, especially among those customers who use remote communication channels. One issue is that most customers still have the desire to talk to a human representative in the customer service center. Another issue is that modern bot technology works effectively in simple conversation scenarios. So, to estimate the potential benefit that automating simple queries can bring, we would need to verify how many simple queries are currently being handled by the contact center. We have to remember, still, that customers want to talk to a human when they have more complex queries that are explicitly related to banking products. This is because, through the prism of trust and a relationship with another person, they feel more comfortable.
How to optimally combine customer support bots with human customer service
Implementing AI services is still profitable once we know the scale of conversations a bot can handle efficiently. To implement AI tools for banks and also meet customer expectations regarding human support, we must prepare customer journeys that consider the synergy between the bot and the contact center representative.
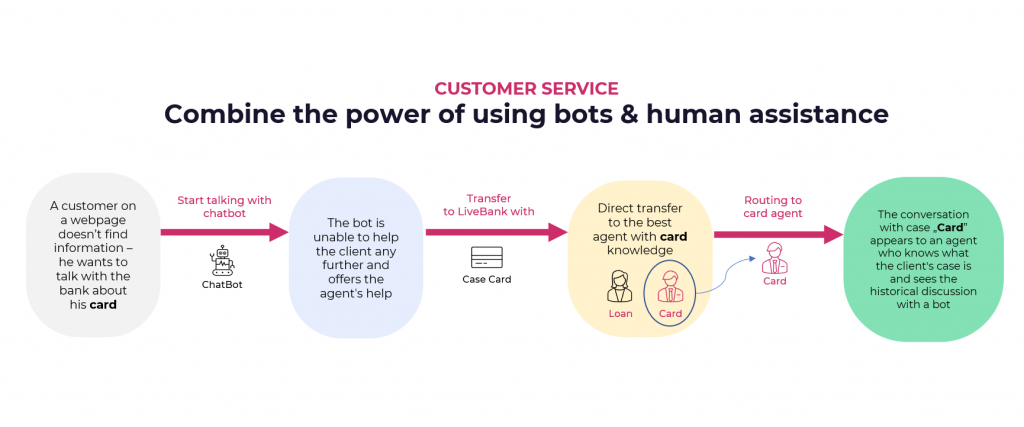
The most effective way to guarantee optimal quality and customer experience is by ensuring the smooth transfer of customers between customer service bots and human representatives. Customers’ expectations will be met if they can continue the conversation with the consultant at the moment when the AI bot is unable to share an answer to their question.
Two critical mistakes to avoid when designing your customer journey
- Changing channels before the customer’s problem is resolved
First of all, customer support bots must always be able to transfer the client to an agent within the service channel that the customer has chosen to engage with. Forcing a customer to use another channel would mean, for example, that customers who prefer to use chat would have to contact telephone support to solve their problem. That is why there must be a smooth client transfer to a consultant in the same channel.
- Not providing the agent with the context from bot interactions
Beware of missing sending the context of the bot’s conversation to the contact centrer representative. This would mean customers would have to repeat the same information regarding their issue, in order to move forward with the conversation. This repetition is likely to cause frustration. Current technological solutions for text conversations are built to handle this problem well. Quality software can succinctly convey any previous discussion with the bot to the representative who comes online to intervene. This allows contact centrer agents to familiarise themselves with the customers’ problems without asking them to describe, again, why they have contacted the bank.
In the end, human and AI customer service in banks is a winning combination
Combining customer service bots with contact centre agent support helps appropriately address customer concerns. When customers feel they can always count on human assistance, they see their chances of getting the help they need increasing. From the bank’s perspective, the powerful combination of human and AI bots help financial institutions use human resources more efficiently and optimise employment-related costs. In addition, high-quality bot technology will transform the quality of contact centre representatives’ work because they will no longer need to repeat monotonous conversations about simple topics and can focus their energy on solving more complex customer problems.



